Introduction: Why Zero Trust Security Matters Now
Cyber threats are no longer the exception—they’re the rule. With the rise of cloud computing, remote work, and sophisticated cyberattacks, businesses cannot rely solely on traditional firewalls and VPNs. This is where Zero Trust Security comes in.
👉 The principle is simple: “Never trust, always verify.” Unlike legacy models that assume everything inside a network is safe, Zero Trust assumes no device, user, or application is trustworthy by default.
According to IBM’s 2024 Cost of a Data Breach Report, organizations with Zero Trust architecture saved nearly $1 million per breach compared to those without it.
What is Zero Trust Security?
Zero Trust Security is a framework that requires strict identity verification for every user and device, regardless of their location inside or outside the network.
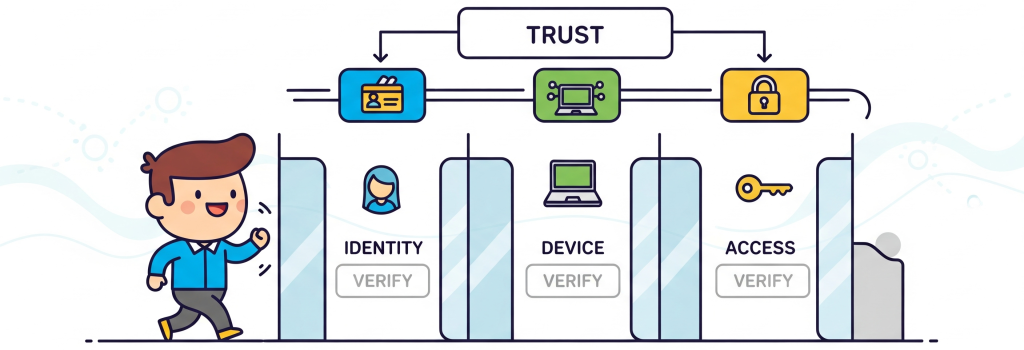
Core Principles of Zero Trust
- Least Privilege Access – Users get only the access they need.
- Continuous Verification – Authentication is ongoing, not one-time.
- Microsegmentation – Breaking networks into smaller zones for added security.
- Real-Time Threat Detection – Monitoring all activity continuously.
The Future of Zero Trust Security in 2025 and Beyond
With AI-driven attacks, ransomware, and remote work culture, Zero Trust is not just a trend—it’s a business necessity.
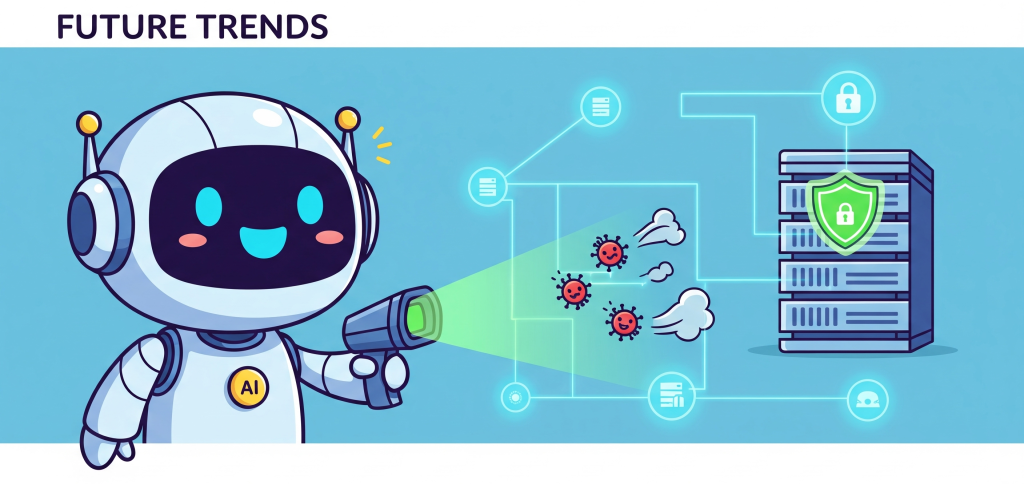

Key Trends Shaping Zero Trust Future
- AI-Powered Security – Leveraging machine learning for anomaly detection.
- Cloud-First Adaptation – Protecting SaaS and hybrid cloud environments.
- IoT & BYOD – Managing risks of personal devices in corporate networks.
- Regulatory Push – Governments enforcing stricter cybersecurity compliance.
💡 Example: The U.S. government’s Executive Order on Cybersecurity requires federal agencies to adopt Zero Trust, setting a global precedent.
Why Businesses Must Embrace Zero Trust
Transitioning to Zero Trust may seem complex, but the long-term advantages outweigh the challenges.
Benefits of Zero Trust Security
- Reduced risk of insider threats
- Improved regulatory compliance
- Enhanced customer trust
- Lower breach costs
- Better scalability with remote work
Challenges Businesses Face
- Implementation complexity
- High initial costs
- Legacy system compatibility issues
- Need for employee training
Transition words like “however,” “therefore,” and “in addition” play a crucial role in making this transition smoother for readability and SEO flow.
How to Implement Zero Trust Security Step-by-Step
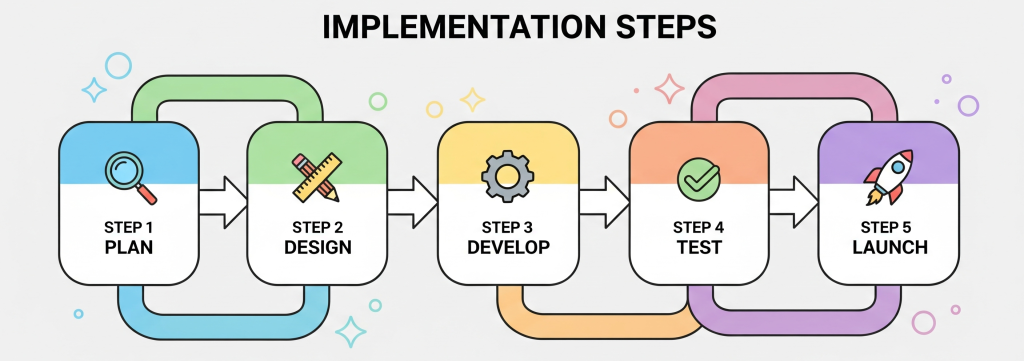
Here’s a structured roadmap businesses can follow:
Step 1: Identify & Classify Assets
Map out sensitive data, users, and applications.
Step 2: Enforce Identity and Access Controls
Use multi-factor authentication (MFA) and single sign-on (SSO).
Step 3: Apply Network Microsegmentation
Break large networks into smaller, secure sections.
Step 4: Monitor & Respond in Real Time
Leverage Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) tools.
👉 For practical guidance, see Microsoft’s Zero Trust Model.
Real-World Use Cases of Zero Trust
- Financial Institutions – Protecting sensitive transaction data.
- Healthcare – Safeguarding patient records.
- E-commerce – Securing online payment systems.
- Remote Work Environments – Controlling access to corporate resources.
Future Outlook: What Businesses Must Prepare For
Zero Trust is evolving with AI, biometrics, and blockchain-based identity management. Businesses must prepare for:
- Stricter compliance laws worldwide
- A shift toward passwordless authentication
- Integration with quantum-resistant security protocols
Conclusion: The Time to Act is Now
Zero Trust is not optional anymore—it’s the foundation of future-ready cybersecurity. Businesses that invest today will gain resilience, customer trust, and compliance readiness tomorrow.
If you want to scale safely in the digital-first era, start planning your Zero Trust journey today.








