Introduction: Why Cybersecurity Matters in Finance
In today’s digital-first world, financial institutions handle billions of transactions daily, from mobile payments to online banking transfers. With this massive growth in digital finance comes a proportional rise in cyber threats. Cybercriminals target banks, fintech firms, and even individual users, making financial industry cybersecurity one of the most critical pillars of trust in the global economy.
👉 For context, according to IBM Security’s Cost of a Data Breach Report, the average cost of a financial data breach reached $5.9 million in 2023. This statistic highlights the urgent need for robust cybersecurity strategies in banking and fintech.
Key Cybersecurity Challenges in the Financial Industry

1. Phishing & Social Engineering
Hackers often use fake emails or websites to steal login credentials and financial data. Even tech-savvy users can fall for well-designed scams.
2. Ransomware Attacks
Banks and financial services are prime targets for ransomware, where criminals lock data and demand payment. Such attacks can paralyze services for days.
3. Insider Threats
Employees with privileged access can unintentionally or deliberately expose sensitive information.
4. Regulatory Compliance Pressure
Financial institutions must adhere to strict rules like GDPR, PCI-DSS, and RBI cybersecurity guidelines. Non-compliance not only risks fines but also damages customer trust.
Best Practices to Protect Digital Transactions
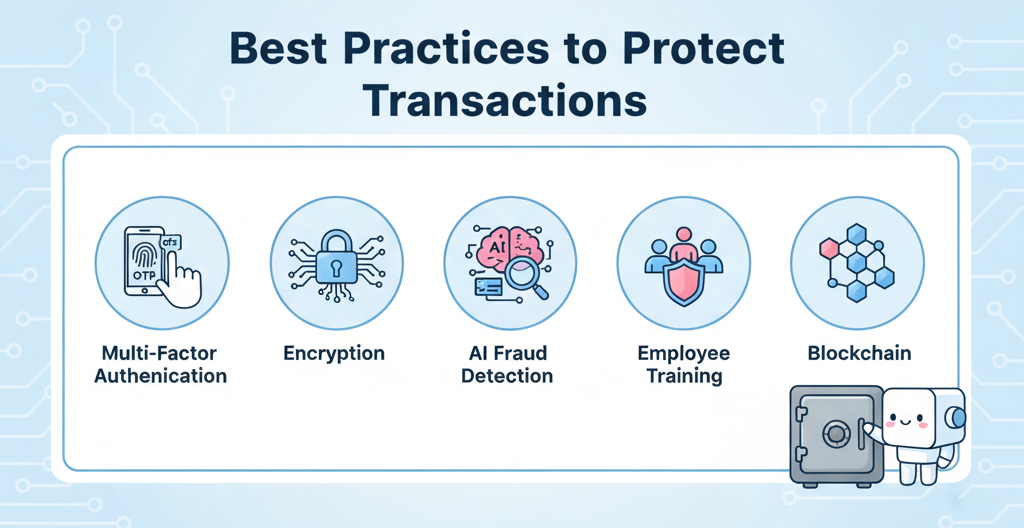
1. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Using MFA ensures that even if hackers steal credentials, unauthorized access is much harder.
2. End-to-End Encryption
Encrypting financial data during transmission prevents interception by malicious actors.
3. AI and Machine Learning for Fraud Detection
AI-powered systems can analyze transaction patterns in real time to detect suspicious activities.
👉 Example: Mastercard’s AI-based fraud detection system saved billions of dollars in fraudulent transactions by identifying anomalies.
4. Employee Training
Human error is a leading cause of breaches. Regular training on phishing awareness and secure data handling is essential.
5. Blockchain for Secure Payments
Blockchain offers immutable transaction records, reducing the risk of fraud and enhancing trust in financial exchanges.
The Role of Regulations in Cybersecurity
Global governments and central banks enforce cybersecurity policies to protect consumers.
- GDPR (Europe) → Protects customer data privacy.
- RBI Cybersecurity Framework (India) → Ensures banks adopt risk-based cybersecurity.
- PCI DSS (Global) → Regulates credit card transaction security.
👉 To explore a detailed guide on cybersecurity compliance, check Kaspersky’s Cybersecurity Insights.
Future of Financial Industry Cybersecurity

1. Quantum-Safe Cryptography
With quantum computing on the horizon, financial institutions must adopt quantum-resistant algorithms.
2. Biometric Authentication
Fingerprint, face, and voice recognition will replace traditional passwords.
3. AI-Driven Threat Intelligence
Banks will increasingly rely on predictive AI tools to prevent attacks before they occur.
4. Cross-Border Cybersecurity Collaboration
Since transactions are global, international security cooperation will be crucial.
Conclusion
The financial industry is the backbone of the global economy, but it is also the top target for cybercriminals. To maintain customer trust, financial institutions must adopt multi-layered cybersecurity strategies, comply with global regulations, and prepare for future technologies like quantum cryptography and AI-driven security.
By prioritizing financial industry cybersecurity, businesses can protect digital transactions, build trust, and stay ahead of evolving threats.








