Introduction
In today’s hyperconnected world, software powers almost every aspect of business—from data management and communication to customer service and operations. However, outdated software security risks often go unnoticed. These vulnerabilities pose major threats to data, reputation, compliance, and operational continuity.
Let’s explore the dangers of outdated software and how automation offers an effective, scalable defense against them.
🔐 The Hidden Dangers of Outdated Software
Outdated software is not just inefficient—it’s unsafe. When vendors stop releasing updates, especially security patches, that software becomes a known target.
Major risks include:
- Known vulnerabilities: Hackers exploit them using automated scripts.
- Lack of vendor support: No help during failures or breaches.
- Compatibility issues: New security protocols may not work with legacy systems.
- Compliance failures: Regulatory frameworks like GDPR, HIPAA, and ISO 27001 require up-to-date software.
Learn more about NIST’s Patch Management Guidelines for compliance.
🛡️ The Real-World Effects of Software Ignorance
According to cybersecurity reports, more than 60% of breaches stem from unpatched systems. These attacks don’t require advanced knowledge nowadays because there are readily available tools that can find out which systems are obsolete and launch exploits in a matter of minutes.
Ransomware attacks, for example, frequently use unpatched vulnerabilities to encrypt files and demand payment. Older software can sometimes even provide hackers administrative access, allow them to steal confidential information, and allow them to roam laterally throughout a whole network.

⚙️ How Automation Changes Cybersecurity Reaction
The rate at which new threats emerge is too fast for manual patching and updates. In cybersecurity, this is where automation can make all the difference.
Automated systems can assist in mitigating the dangers associated with obsolete software in the following ways:
1. Patch Management Automation
Automation technologies automatically apply security fixes with little downtime after routinely scanning for version numbers and identified flaws. This speeds up the entire upgrade lifecycle as well as avoids human error.
2. Detecting Threats in Real Time
AI-driven security solutions continuously track system activity. They immediately initiate alarms or isolation procedures when they identify irregularities brought on by out-of-date components.
3. Reports on Automated Compliance
Automation systems can produce current compliance reports, monitor software lifecycles, and guarantee conformance with audit criteria for industries subject to regulatory frameworks.
4. Self-Repair Mechanisms
Uptime and safety can be kept together by certain complex platforms that can recognize a malfunctioning or unsafe application instance and proactively fall it in or reset it to a clean version.
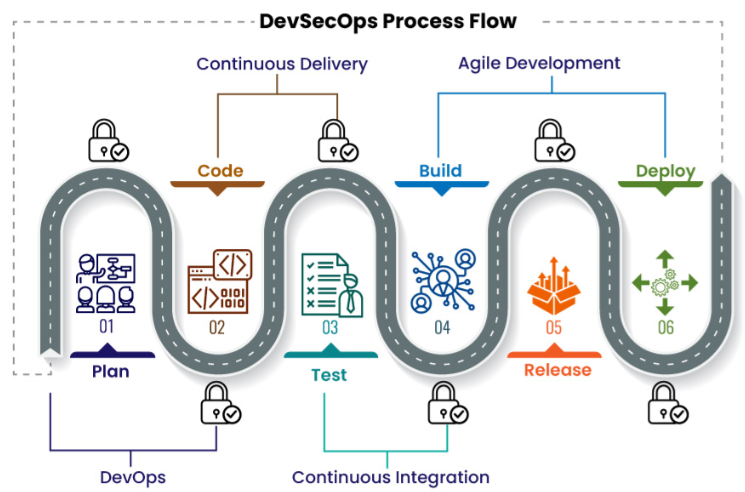
🧠 DevSecOps and AI: Automation’s Function in the Larger Scheme
Security is no longer only the responsibility of the IT department. As DevSecOps has grown in popularity, businesses are incorporating security into all stages of the software development process. From development to deployment, developers can use automation tools to set safety rules, scan code, and keep an eye on dependencies.
Additionally, machine learning is improving automated threat detection by spotting trends that humans would overlook, like threats from insiders or low-and-slow attacks.
🏗️ Developing a Security Strategy That Is Future – Ready
If you continue to manage patches using spreadsheets and handwritten checklists, your company is vulnerable. The solution isn’t just updating your software—it’s building a resilient, automated defense infrastructure that grows with your business and threat landscape.
Here are some doable actions to take:
- Put in place automated mechanisms for vulnerability screening and patching.
- Make software lifecycle management a part of your security guidelines.
- Teach DevSecOps techniques to teams.
- To identify threats proactively, spend money on anomaly detection powered by AI.

Conclusion
Outdated software is a silent danger that lurks in the shadows. However, automation provides businesses with a strong defense to maintain the security, compliance, and refreshes of their technology without continual human supervision. Automation is becoming a need rather than a luxury as digital ecosystems get increasingly complicated.
By embracing automation now, organizations are not just lowering risk but also securing their cybersecurity frameworks for the future.








