Introduction: The Invisible Threat Within Your Own Walls
In today’s fast-paced digital world, employees seek instant solutions to meet deadlines and improve productivity. However, this convenience often leads to a growing and dangerous trend known as Shadow IT security risks — the silent use of unauthorized apps, tools, or devices within organizations. The term refers to the use of unauthorized applications, software, or devices within an organization’s IT ecosystem without the knowledge or approval of the IT department.
While it may seem harmless—like using a free file-sharing app or unapproved cloud storage—Shadow IT can silently expose your organization to data breaches, compliance violations, and cyberattacks.
👉 According to a study by Gartner, over 40% of IT spending in large enterprises happens outside official IT budgets, revealing the sheer scale of this hidden problem.
For more insights on similar cybersecurity challenges and solutions, visit BotDef Blog—a platform sharing awareness on technology and security trends.
What Exactly Is Shadow IT?
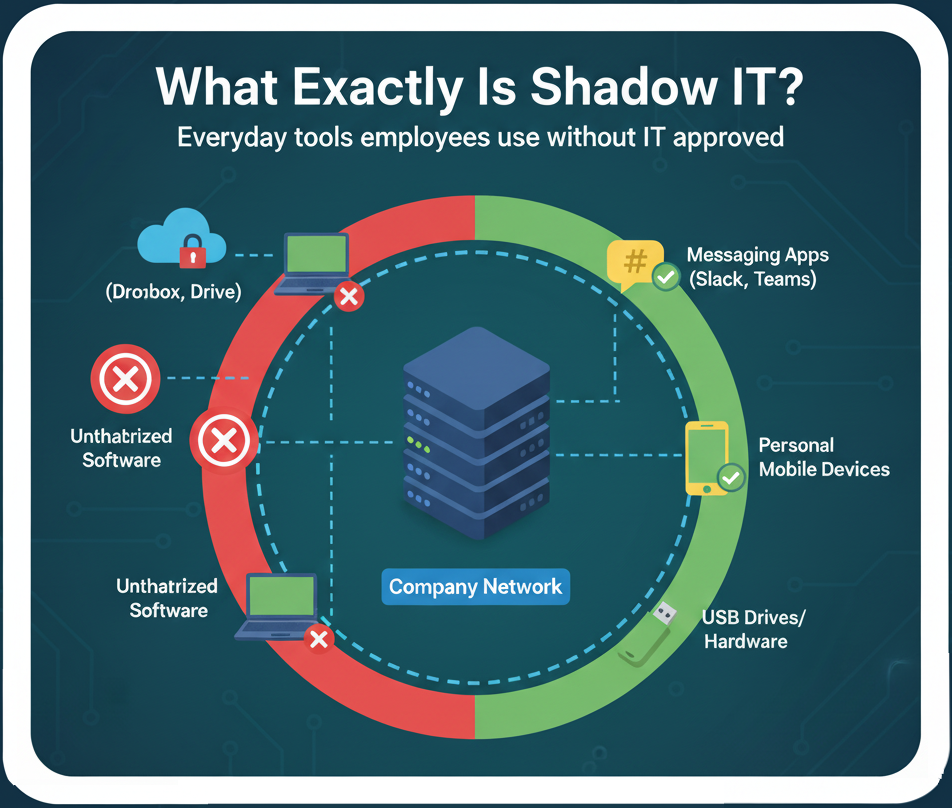
Shadow IT encompasses any technology used within an organization without formal approval. This includes:
- Cloud storage services like Dropbox, Google Drive, or WeTransfer used for sharing files.
- Communication tools such as WhatsApp or Slack for unofficial conversations.
- Unapproved SaaS applications for project management or productivity tracking.
- Personal devices (BYOD) connected to the company network without security clearance.
While these tools offer convenience, they bypass IT controls, making data visibility and protection nearly impossible.
Why Shadow IT Is a Hidden Security Risk
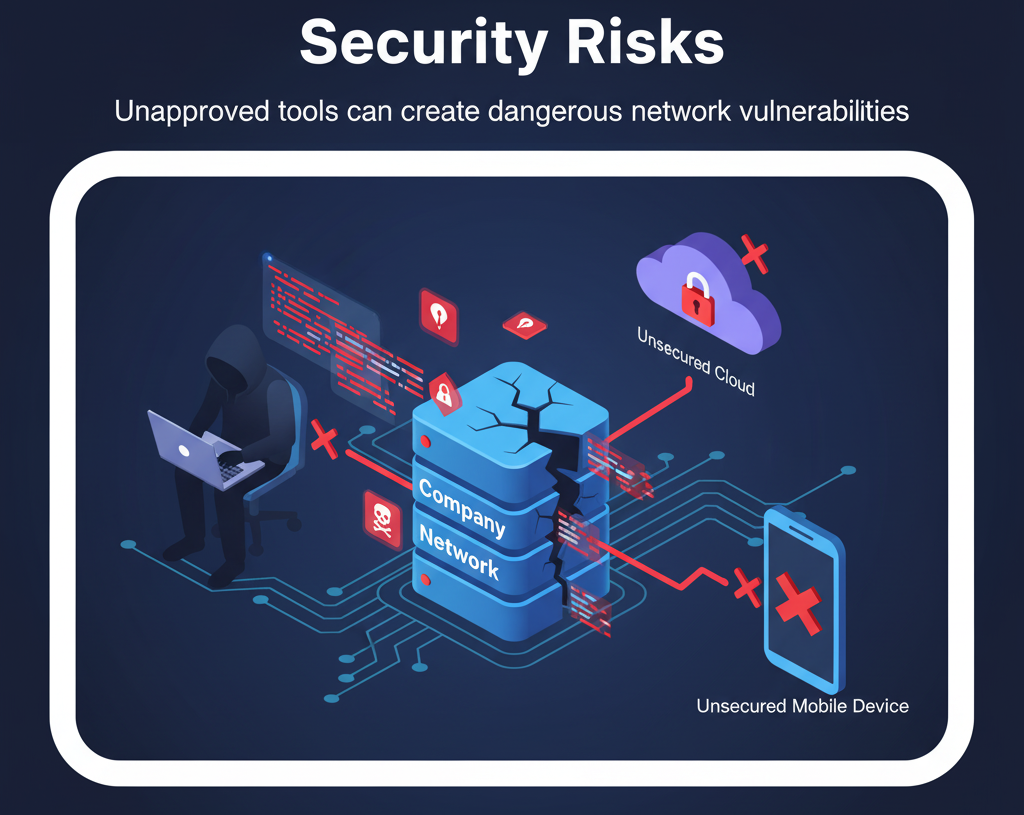
Despite good intentions, employees using unapproved tools can cause massive vulnerabilities. Here’s how:
1. Data Breaches and Loss
Unsecured cloud apps or devices may store sensitive business data outside corporate firewalls, increasing the risk of unauthorized access. Once data leaves the company network, it’s nearly impossible to track or retrieve.
2. Compliance Violations
Industries bound by regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, or ISO 27001 must maintain strict data handling standards. Shadow IT undermines compliance, leading to heavy penalties and loss of client trust.
3. Lack of Visibility
When IT teams are unaware of unauthorized tools, they can’t protect or monitor them. This lack of oversight creates blind spots that cybercriminals exploit to infiltrate systems.
4. Increased Attack Surface
Every unapproved device or app connected to the network expands the organization’s attack surface, giving hackers more entry points.
5. Financial Damage
Recovering from a Shadow IT-related breach often costs more than prevention. Loss of reputation, downtime, and fines can significantly impact business continuity.
The Psychology Behind Shadow IT
Many employees don’t intentionally break rules. They simply look for faster tools to improve efficiency. The main drivers behind Shadow IT are:
- Convenience: Easy access to free tools online.
- Lack of Awareness: Employees don’t realize the risks involved.
- Slow IT Approval Process: Lengthy internal approvals push employees to use what’s easily available.
- Remote Work Culture: Home networks and personal devices are less secure, increasing unsupervised tool usage.
Creating awareness about these factors through internal training programs can reduce Shadow IT incidents dramatically.
How to Identify and Manage Shadow IT

Organizations can’t fight what they can’t see. The key is to detect, manage, and prevent unauthorized technology usage.
Step 1: Conduct IT Audits Regularly
Use network monitoring tools to identify unknown applications or data transfers. Periodic audits help spot patterns of unsanctioned software usage.
Step 2: Implement Centralized Access Management
Adopt Identity and Access Management (IAM) solutions to control user access. Restrict app usage based on predefined roles and permissions.
Step 3: Create an Approved Software List
Maintain a transparent catalog of sanctioned tools and ensure all employees are aware of it. This minimizes accidental use of unapproved apps.
Step 4: Educate Employees Continuously
Awareness programs are crucial. Encourage employees to report new tool requests and explain how unapproved apps can harm the organization.
Step 5: Strengthen Cloud Security Policies
Since Shadow IT often involves cloud services, define strict data sharing and storage policies for all departments.
Technologies to Combat Shadow IT
Organizations can leverage modern cybersecurity tools to detect and manage Shadow IT efficiently:
- CASB (Cloud Access Security Broker): Monitors cloud usage and prevents unauthorized access.
- DLP (Data Loss Prevention) Systems: Detects and blocks the transfer of sensitive information outside the organization.
- SIEM (Security Information and Event Management): Provides real-time monitoring and alerts for suspicious activities.
- Endpoint Protection Platforms: Safeguard personal and corporate devices from external threats.
For more technology-based insights, explore similar cybersecurity topics at BotDef’s Tech Awareness Blog.
Future of Shadow IT: Adapting to a Zero-Trust World
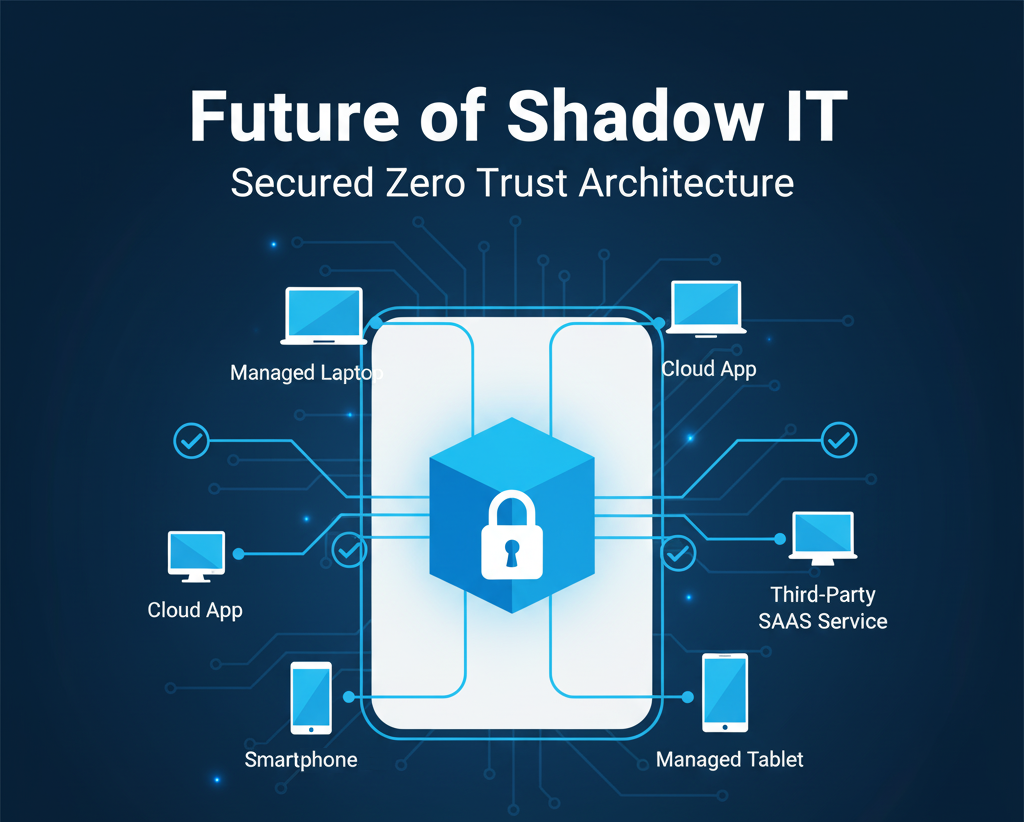
The future of cybersecurity lies in Zero Trust Architecture—a framework where no device, user, or system is trusted by default. Implementing Zero Trust principles ensures every connection request is verified, significantly reducing the impact of Shadow IT.
As businesses continue to adopt remote and hybrid work models, managing Shadow IT will become a core element of corporate cybersecurity strategies.
For a deeper understanding of the Zero Trust model, you can read our detailed blog: The Future of Zero Trust Security: What Businesses Must Know.
Conclusion: Transform the Threat into Awareness
Shadow IT isn’t just a technological challenge—it’s a behavioral and cultural issue. Organizations that encourage open communication, transparency, and continuous training can turn this hidden risk into an opportunity for stronger cybersecurity posture.
Ultimately, it’s not about restricting innovation—it’s about enabling it safely. By balancing employee autonomy with IT governance, you can ensure that Shadow IT becomes a managed ally, not a lurking threat.








