Introduction: The Growing Threat in E-commerce
E-commerce has transformed the way businesses operate, enabling global transactions with just a few clicks. However, why e-commerce platforms are prime targets for hackers is a question every business must consider. These platforms store valuable data, making them highly attractive for cybercriminals. Hackers increasingly target e-commerce platforms because they hold sensitive financial, personal, and transactional data. According to IBM’s 2025 Cost of a Data Breach Report, the retail and e-commerce sector remains one of the most vulnerable industries.
In this blog, we’ll explore why hackers target e-commerce platforms, the techniques they use, the consequences for businesses, and how to prevent cyberattacks.
Why E-commerce Platforms Attract Hackers
High-Value Financial Transactions
E-commerce websites process thousands of transactions daily. Each transaction involves credit card details, bank account numbers, and payment gateway credentials. Hackers see this as an easy opportunity for theft and fraud.
Personal Data as Digital Gold
Beyond financial details, e-commerce stores also store:
- Names
- Addresses
- Contact numbers
- Login credentials
This personal information can be sold on the dark web or used in phishing scams.
Third-Party Integrations and Weak Links
E-commerce platforms often rely on plugins, third-party apps, and APIs. A single vulnerability in these integrations can compromise the entire system.
Common Hacking Techniques in E-commerce
Phishing Attacks
Hackers trick customers with fake emails, imitating legitimate e-commerce stores, to steal login and payment details.
DDoS Attacks
Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) floods a website with traffic until it crashes. This disrupts sales and damages customer trust.
SQL Injection
By exploiting poorly coded databases, hackers can access usernames, passwords, and credit card details.
Malware and Ransomware
Hackers inject malicious code into websites, stealing customer data or encrypting files until ransom is paid.
The Consequences of E-commerce Hacking
- Financial Losses – Businesses face chargebacks, refunds, and revenue loss.
- Downtime – A hacked website can stay offline for hours or days.
- Reputation Damage – Customers lose trust and shift to competitors.
- Legal and Compliance Risks – Violations of GDPR or PCI DSS can result in heavy fines.
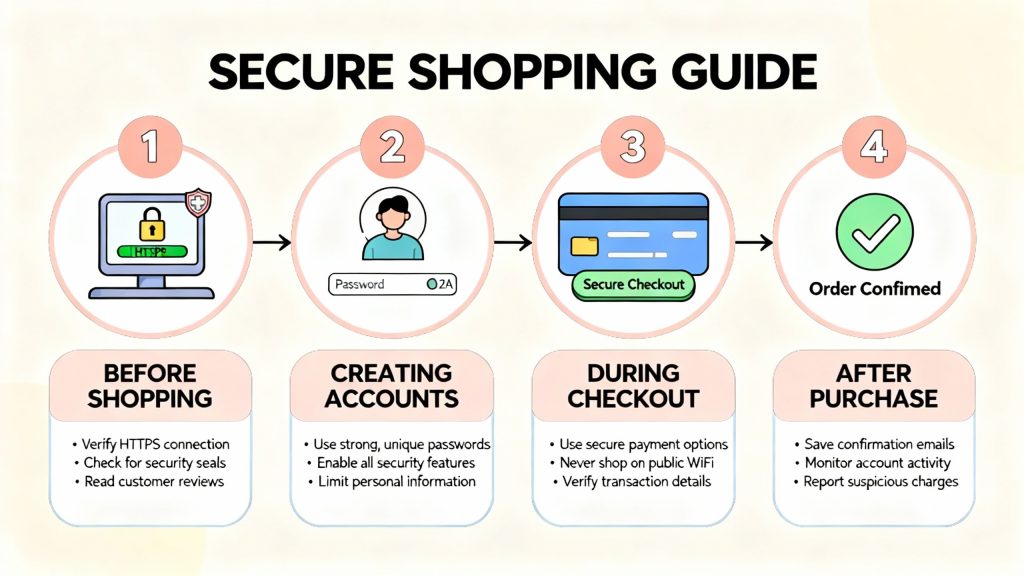
How to Protect E-commerce Platforms
Implement Strong Security Practices
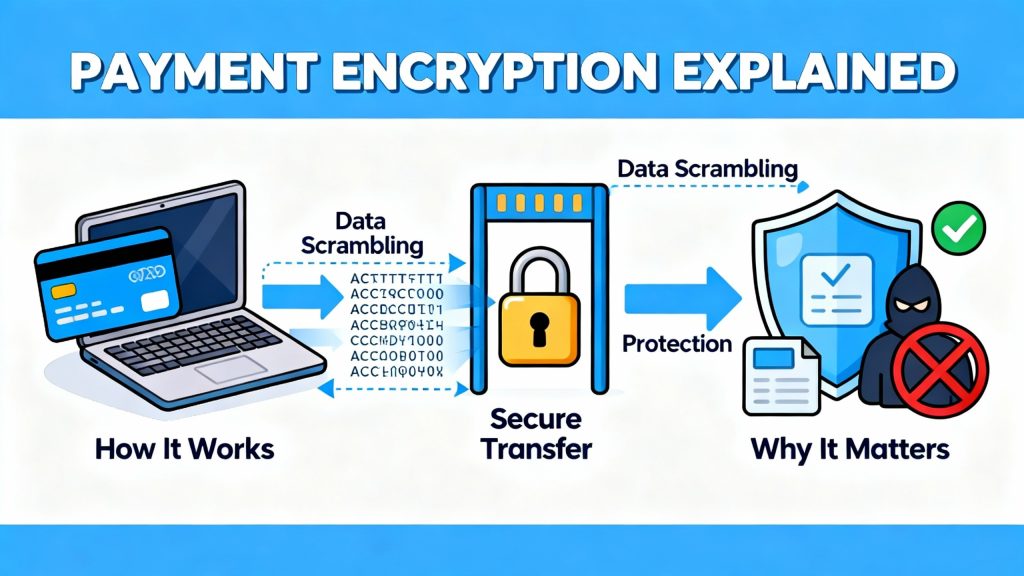
- Use SSL encryption
- Enforce two-factor authentication (2FA)
- Regularly update plugins, APIs, and payment gateways
Conduct Regular Security Audits
Routine penetration testing helps uncover hidden vulnerabilities.
Educate Customers and Staff
Awareness about phishing, weak passwords, and safe browsing habits reduces risks.
Secure Payment Gateways
Work with trusted providers like PayPal or Stripe that meet strict compliance standards.
Future of Cybersecurity in E-commerce
With the growth of AI-powered attacks and quantum computing, businesses must adopt advanced solutions. Future e-commerce security will rely heavily on:
- AI-based fraud detection
- Blockchain-powered transactions
- Zero-trust security frameworks
According to Cybersecurity Ventures, global cybercrime costs will hit $10.5 trillion annually by 2025 — making e-commerce protection more urgent than ever.
Conclusion
E-commerce platforms are prime hacker targets because of their valuable financial and personal data. However, by adopting strong cybersecurity measures, educating users, and preparing for future threats, businesses can minimize risks and build long-term trust with their customers.








