Cybersecurity is no longer about defending the perimeter. In today’s hyperconnected world, Zero Trust architecture has become the gold standard for protecting digital assets. Instead of assuming everything inside a network is safe, Zero Trust eliminates implicit trust and verifies every access request—regardless of origin.
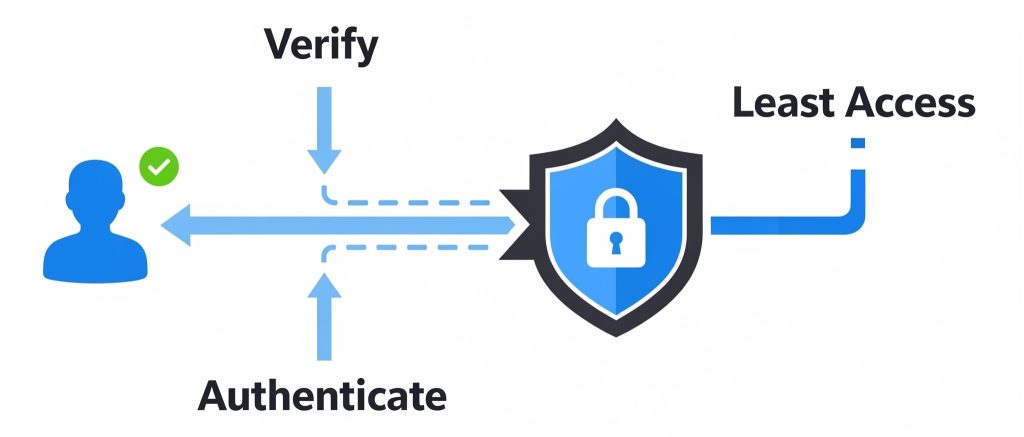
What Is Zero Trust in Cybersecurity?
At its core, Zero Trust means “never trust, always verify.” It’s a security model that authenticates and authorizes every user and device before granting access, even within the network itself.
Key Principles of Zero Trust:
- Verify explicitly — Always authenticate access.
- Use least privilege access — Minimize user permissions.
- Assume breach — Always monitor and log user behavior.
🔗 Reference: NIST Zero Trust Architecture Model
Why Traditional Security Models Are Failing
Previously, firewalls and VPNs protected the network perimeter. However, with remote work, cloud computing, and BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) policies, the traditional model is no longer sufficient.
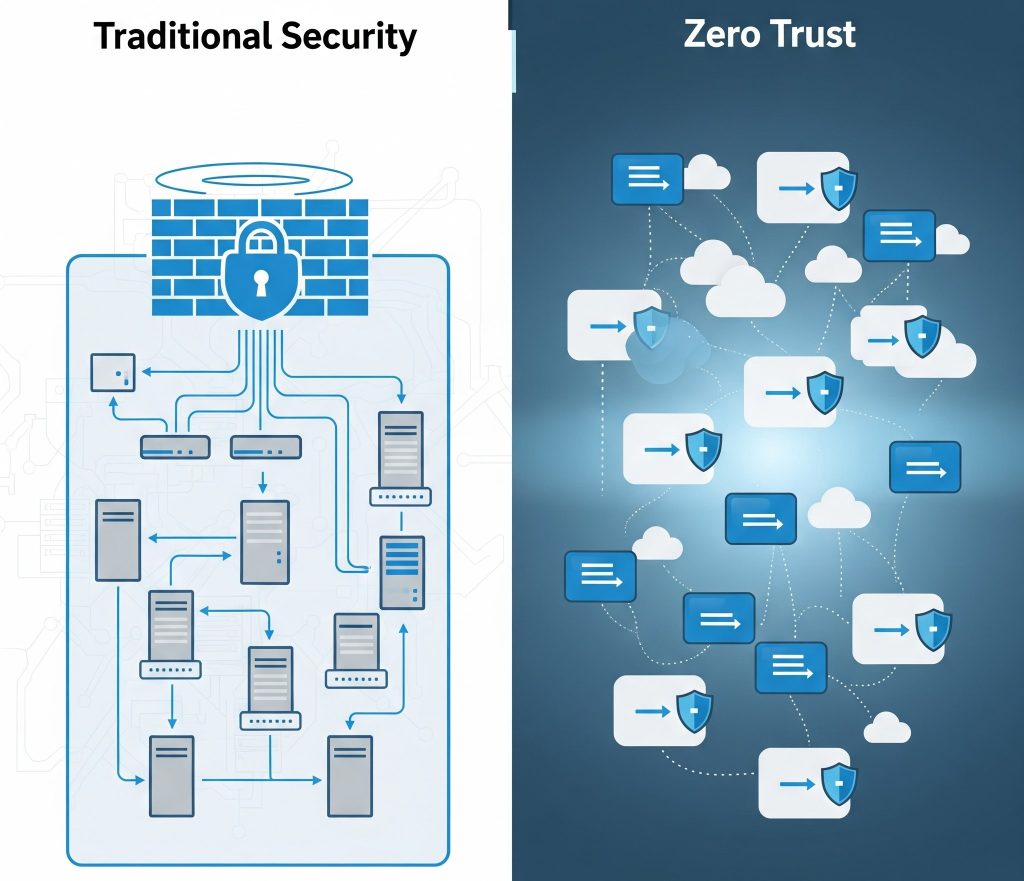
💬 For instance, once an attacker breaches the perimeter, they can move laterally across systems. Zero Trust stops this by constantly validating identities.
How Zero Trust Is Reshaping Cyber Defense
Zero Trust doesn’t just enhance security—it revolutionizes it. Here’s how:
1. Micro-Segmentation
Breaks the network into small zones to control access to sensitive data.
2. Continuous Monitoring
Tracks user behavior, anomalies, and risks in real-time.
3. Strong Authentication
Utilizes MFA (Multi-Factor Authentication), biometrics, and identity providers.
Benefits of Implementing Zero Trust
Transitioning to Zero Trust offers a host of benefits:
- Minimizes attack surface
- Enhances cloud security
- Improves regulatory compliance
- Strengthens visibility & control
Moreover, organizations report faster breach detection and improved incident response times after adopting this architecture.
Challenges to Overcome
Of course, Zero Trust implementation comes with its own set of challenges:
- Complex architecture restructuring
- Initial investment cost
- Organizational resistance to change
However, with proper planning and stakeholder buy-in, these hurdles can be overcome.
Zero Trust in Action: Real-World Example
Companies like Google (BeyondCorp) and Microsoft have adopted Zero Trust principles. Their success stories highlight how modern cybersecurity can thrive without traditional borders.
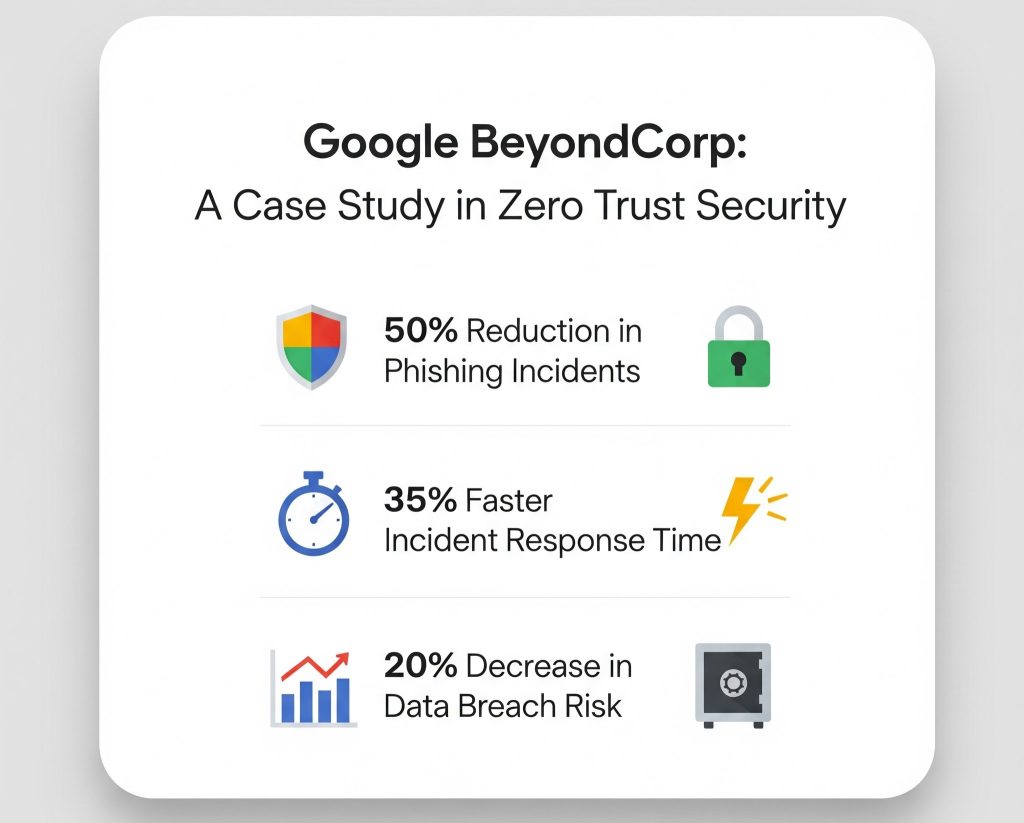
✅ A notable example is Google’s BeyondCorp, which secures access to internal apps without VPNs, leveraging Zero Trust at scale.
Best Practices to Start with Zero Trust
If you’re considering Zero Trust, here’s how to begin:
Conduct a Security Audit
Assess your current IT environment.
Implement Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Prioritize secure access controls.
Apply MFA and Endpoint Detection
Protect each point of entry.
Train Your Team
Security awareness is key to success.
Final Thoughts: Zero Trust Is the Future of Cybersecurity
As cyber threats continue to evolve, Zero Trust provides a proactive, resilient approach. It doesn’t rely on outdated assumptions. Instead, it adapts to modern threats, making it a vital strategy for every organization in 2025 and beyond.
Whether you’re a small startup or a global enterprise, adopting Zero Trust isn’t just a choice—it’s a necessity for survival in today’s digital age.








